Kidney beans are a highly nutritious legume, traceable back to Mesoamerican civilizations around 7000 BCE, and have long been recognized for their health benefits. They are particularly rich in protein and fiber, making them an excellent choice for individuals on plant-based diets, as well as for those with diabetes or who wish to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Their low-fat profile and lack of cholesterol support heart health by aiding in the reduction of cholesterol through their soluble fiber content. To maximize nutrient absorption and reduce anti-nutrients, it is recommended to soak dried kidney beans overnight before cooking them until tender. Cooking methods can be varied, including boiling, steaming, or pressure cooking, with the addition of spices like cumin, garlic, and onion powder for flavor and extra health benefits. Seasoning with a pinch of baking soda during cooking can also aid digestibility by neutralizing compounds that cause gas. Incorporating kidney beans into a balanced diet enhances overall health, promotes heart health, and aligns with the ethos of a plant-based lifestyle, offering a versatile and nutrient-dense option for a variety of dishes.
Embark on a delightful journey into the heart of culinary history with our exploration of kidney beans—a legume that has been a staple in diets around the globe for millennia. This article delves into the rich tapestry of kidney bean origins, uncovering their ancient roots and tracing their cultivation from their native Americas to present-day kitchens worldwide. As we chart the nutritional profiles and health benefits of these versatile beans, we’ll highlight their role in a plant-based diet, particularly emphasizing how they aid in cholesterol management and blood sugar control. Discover various cooking methods that enhance both flavor and digestibility, and indulge in a global palette of kidney bean recipes. From traditional preparations to modern techniques, this article offers a comprehensive guide to selecting, storing, and incorporating kidney beans into a wide array of dishes. Join us as we unravel the science behind their digestion, examine their role in sustainable agriculture, and anticipate future innovations that promise to elevate these humble yet mighty beans to new heights.
- Unraveling the Origins of Kidney Beans: A Journey Through Time and Cultivation
- Kidney Beans' Nutritional Profiles and Health Benefits
- The Role of Kidney Beans in a Plant-Based Diet
- Cooking Kidney Beans: Methods and Variations to Enhance Flavor and Digestibility
- Kidney Beans and Cholesterol: Understanding the Relationship
Unraveling the Origins of Kidney Beans: A Journey Through Time and Cultivation
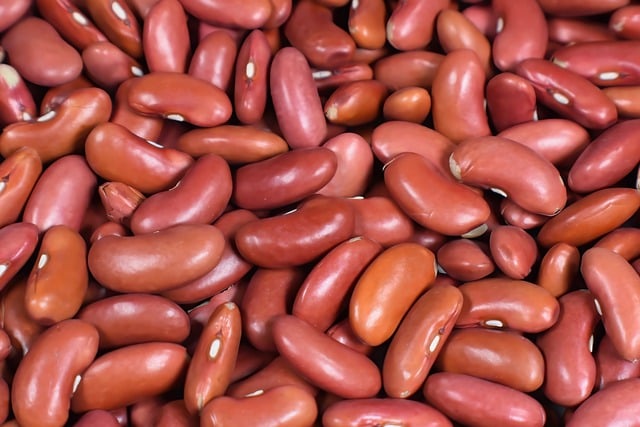

The origins of kidney beans trace back to Mesoamerica, with evidence of their cultivation as far back as 7000 BCE among indigenous peoples in what is now Mexico and Central America. These legumes were a staple in the diets of various cultures, including the Mayans and Aztecs, who recognized their significant health benefits. Kidney beans are rich in protein and fiber, making them an excellent choice for individuals following a plant-based diet, and they are particularly beneficial for those managing cholesterol levels. Their nutrient profile also contributes to effective blood sugar control, which is a boon for diabetes management or for anyone interested in maintaining steady energy levels.
The journey of kidney beans from their Mesoamerican roots to the global stage is a testament to their adaptability and culinary versatility. Today, they are grown in numerous regions around the world, including the United States, India, and China. The health benefits associated with kidney beans have been well-documented: they are low in fat, high in nutrients, and can be included in a variety of dishes to enhance both flavor and nutrition. When preparing kidney beans, it is important to follow proper cooking techniques to ensure their digestibility and safety; improper handling can lead to gastric discomfort. Various methods for cooking kidney beans abound, from simple boiling to more complex recipes that incorporate a myriad of spices and ingredients, allowing culinary enthusiasts to explore the rich history of this legume while enjoying its healthful properties.
Kidney Beans' Nutritional Profiles and Health Benefits

Kidney beans, with their distinctive shape and versatile culinary applications, offer a wealth of health benefits that have cemented their place in many dietary regimens around the globe. These legumes are not only a staple in various cuisines but also provide an impressive nutritional profile. A single cup of cooked kidney beans contains approximately 15 grams of protein, making them an excellent plant-based source for those following or interested in a plant-based diet. Moreover, they are rich in dietary fiber, which is essential for digestive health and can aid in preventing constipation and promoting regular bowel movements. The high fiber content also contributes to the slow absorption of carbohydrates, which is beneficial for blood sugar control, making kidney beans a suitable food choice for individuals with diabetes or those aiming to manage their blood sugar levels.
Incorporating kidney beans into your diet can contribute significantly to your health. They are low in fat and devoid of cholesterol, thus making them heart-healthy. The soluble fiber in kidney beans can help lower cholesterol levels by binding with cholesterol-rich bile acids in the digestive system and helping to remove them from the body. Additionally, these beans are a good source of several vital nutrients, including iron, potassium, and B vitamins, which support overall health. When preparing kidney beans, it’s important to cook them properly to maximize their nutritional benefits; soaking them overnight and then boiling can reduce antinutrients like phytates that may otherwise interfere with the absorption of certain minerals. Numerous recipes for cooking kidney beans exist, from traditional chili and stews to modern salads and side dishes, ensuring that this nutrient-dense food remains a delightful addition to any meal.
The Role of Kidney Beans in a Plant-Based Diet

Kidney beans have long been a staple in plant-based diets due to their high nutritional value and versatility in various cuisines. As legumes, they are an excellent source of plant-based protein, which is crucial for muscle repair and growth, making them a valuable inclusion for those adhering to or exploring a plant-based diet. Moreover, these beans are rich in fiber, a nutrient that aids in digestion and can help maintain healthy blood sugar levels, a benefit particularly relevant for individuals with diabetes or those seeking to manage their blood sugar more effectively. The high fiber content also contributes to the satiety factor, which can be beneficial for weight management. From a health standpoint, kidney beans are low in fat and devoid of cholesterol, which aligns well with the goals of a plant-based diet that seeks to minimize the intake of saturated fats and cholesterol often found in animal products.
Incorporating kidney beans into meals is straightforward and can be tailored to diverse culinary preferences. They can be boiled, steamed, or pressure-cooked for a tender texture and can be easily added to salads, soups, stews, and burritos. For those interested in how to cook kidney beans, it’s essential to soak them overnight to reduce anti-nutrients like phytates and tannins, which can inhibit nutrient absorption. After soaking, draining, and rinsing, they can be cooked with fresh water until tender. The health benefits of kidney beans are myriad, including their role in reducing the risk of heart disease by lowering cholesterol levels due to their soluble fiber content. Additionally, their antioxidant properties help combat oxidative stress, a condition that can contribute to various chronic diseases. Including kidney beans as part of a plant-based diet can thus be a simple yet impactful choice for enhancing overall health and well-being.
Cooking Kidney Beans: Methods and Variations to Enhance Flavor and Digestibility
Including kidney beans in your diet can be a delightful and nutritious choice, offering numerous health benefits. These legumes are celebrated for their contributions to heart health by helping to manage cholesterol levels. The soluble fiber in kidney beans binds with fats and bile acids, promoting their excretion from the body and reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Moreover, they are a treasure trove for those following a plant-based diet, providing a substantial source of protein and complex carbohydrates that aid in blood sugar control.
When cooking kidney beans, there are various methods to enhance both flavor and digestibility. Soaking beans overnight and discarding the soaking water can significantly reduce antinutrients like phytic acid, which may otherwise impede nutrient absorption. After soaking, rinsing the beans well is a crucial step before cooking. To cook kidney beans, bring them to a boil with fresh water, then reduce the heat to a simmer. This process allows for tender beans while preserving their nutritional content. Seasoning your beans with herbs and spices can amplify their rich flavor profile. For example, cumin, garlic, and onion powder not only make the beans more appetizing but also offer additional health benefits, such as anti-inflammatory properties. To further aid digestibility, some suggest adding a pinch of baking soda to the cooking water, which can help neutralize gas-causing sugars. Whether you prefer a simple preparation with just salt and pepper or a more elaborate dish seasoned with various spices, the key to enjoying kidney beans lies in finding the balance that suits your palate while maximizing their healthful attributes.
Kidney Beans and Cholesterol: Understanding the Relationship

Kidney beans have long been recognized for their health benefits, particularly in the context of managing cholesterol levels and supporting a plant-based diet. Including kidney beans in your regular diet can be advantageous for cardiovascular health due to their soluble fiber content, which has been shown to bind with cholesterol in the digestive system and prevent its absorption into the bloodstream. This binding action plays a crucial role in reducing overall cholesterol levels, thereby mitigating the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular conditions. For those on a plant-based diet or looking to adopt one, kidney beans are an excellent source of protein and complex carbohydrates, offering a nutrient-dense alternative to animal products. They contribute to blood sugar control by providing a steady release of glucose, which is beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those seeking to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Cooking kidney beans properly is essential to maximize their health benefits and ensure digestibility. To prepare them, soak dried kidney beans overnight, then rinse and cook until tender. They can be incorporated into a myriad of dishes, from salads and stews to soups and side dishes, making them versatile and easy to include in a healthful diet. Whether you’re aiming to lower cholesterol or looking for heart-healthy meal options, kidney beans are a valuable addition to any plant-based menu. Their high nutrient content, including vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, complements their ability to support overall health when consumed as part of a balanced diet.
Kidney beans, with their storied origins and rich nutritional content, have long been a staple in diets around the globe. This exploration into the history and benefits of kidney beans has revealed not only their ancient roots but also their significant role in modern, health-conscious eating. From their exceptional nutritional profiles and contributions to a plant-based diet, to their ability to aid in blood sugar control and help reduce cholesterol levels, kidney beans stand out as a versatile and beneficial legume. The various cooking methods and flavorful variations presented ensure that these beans remain a delightful addition to any meal. As we continue to celebrate and utilize this humble yet mighty food source, it is clear that kidney beans will remain a valued component of nutritious and sustainable eating for generations to come.



